Understanding Diabetic Gastroparesis: Symptoms and Treatment Options
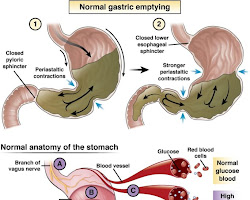
Diabetic gastroparesis is a digestive disorder that affects individuals with diabetes, impacting the normal movement of food through the stomach. The condition occurs when the vagus nerve, responsible for controlling the stomach muscles, is damaged or weakened due to long-term high blood sugar levels. In this blog post, we’ll explore the symptoms and treatment options for diabetic gastroparesis, empowering individuals with diabetes to manage this challenging complication effectively.
1. Symptoms of Diabetic Gastroparesis
Diabetic gastroparesis can lead to a range of uncomfortable symptoms, including:
- Nausea and Vomiting: Delayed stomach emptying can cause food to sit in the stomach for longer periods, leading to persistent nausea and vomiting.
- Feeling Full Quickly: Individuals may feel full even after consuming small amounts of food, making it challenging to maintain proper nutrition.
- Bloating and Abdominal Discomfort: Gastroparesis can cause bloating and discomfort in the upper abdomen.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Due to decreased food intake and delayed stomach emptying, unexplained weight loss may occur.
- Erratic Blood Sugar Levels: Gastroparesis can lead to unpredictable blood sugar levels, making diabetes management more challenging.
2. Treatment Options
While diabetic gastroparesis cannot be completely cured, various treatment options can help manage the symptoms and improve overall well-being:
a. Dietary Changes: Adjusting the diet is essential in managing gastroparesis symptoms. Eating smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding high-fat and high-fiber foods can ease digestion.
b. Medications: Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to help regulate stomach contractions and alleviate symptoms.
c. Insulin Adjustments: For individuals with diabetes, insulin adjustments may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels in response to delayed stomach emptying.
d. Prokinetic Agents: Prokinetic medications can help improve stomach motility and facilitate better food movement.
e. Gastric Emptying Procedures: In severe cases, gastric emptying procedures may be considered to help regulate food movement from the stomach.
f. Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, stress management, and smoking cessation, can support overall digestive health.
3. Tips for Managing Diabetic Gastroparesis
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly check blood sugar levels to understand how gastroparesis affects glucose control.
- Keep a Food Diary: Keeping track of food intake and symptoms can help identify triggers and develop a suitable meal plan.
- Chew Food Thoroughly: Chewing food thoroughly can ease the digestive process and reduce the strain on the stomach.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, but avoid drinking large amounts of liquids with meals.
Diabetic gastroparesis can be a challenging complication for individuals with diabetes, affecting digestion and blood sugar management. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking early medical intervention is crucial to prevent complications and enhance quality of life. By making dietary adjustments, following prescribed medications, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals with diabetic gastroparesis can better manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance, as managing diabetic gastroparesis requires an individualized approach. With proper care and attention, individuals with diabetic gastroparesis can effectively navigate this condition and continue to thrive in their diabetes management journey.