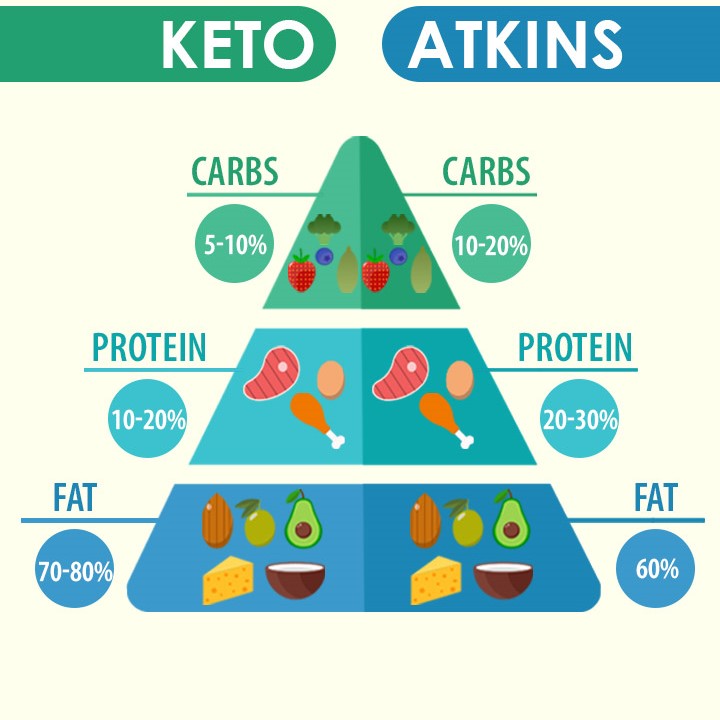
The world of low-carb diets offers a variety of options for those looking to shed pounds, manage blood sugar, or improve overall health. Two prominent choices in this category are the ketogenic diet and the modified Atkins diet. While both restrict carbohydrates, they differ in some key aspects. In this article, we’ll break down the differences between these two low-carb diets,Ketogenic Diet vs. Modified Atkins Diet explore their benefits and considerations, provide external links for further research, and answer frequently asked questions to help you choose the one that suits your health and lifestyle goals.
The Ketogenic Diet: A High-Fat, Low-Carb Lifestyle
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as “keto,” is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet designed to put the body into a state of ketosis. This metabolic state encourages the body to burn fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. Key features of the ketogenic diet include:
- High Fat: Approximately 70-75% of daily calories come from healthy fats.
- Low Carbohydrates: Carbohydrate intake is restricted to about 5-10% of daily calories.
- Moderate Protein: Protein intake is moderate, accounting for around 15-20% of daily calories.
The Modified Atkins Diet: A Low-Carb Alternative
The modified Atkins diet, also known as “MAD,” is another low-carb diet that shares some similarities with the ketogenic diet. It’s less restrictive in terms of fat intake but still promotes carbohydrate reduction. Key features of the modified Atkins diet include:
- Moderate Fat: Unlike the ketogenic diet, the modified Atkins diet is less strict about fat consumption, allowing for a more moderate fat intake.
- Low Carbohydrates: Carbohydrate intake is also limited, but the restriction may not be as severe as in the ketogenic diet.
- Moderate to High Protein: The modified Atkins diet often allows for more protein than the ketogenic diet, typically accounting for 20-30% of daily calories.
Comparing the Ketogenic Diet and Modified Atkins Diet
Weight Loss and Metabolic Goals
- Ketogenic Diet: Designed for rapid weight loss and therapeutic purposes, such as managing epilepsy and diabetes.
- Modified Atkins Diet: Suitable for weight management and potential health improvements, with a more flexible approach to fat intake.
Ketosis
- Ketogenic Diet: Emphasizes strict ketosis, requiring precise macronutrient ratios to maintain the state.
- Modified Atkins Diet: May not induce or maintain ketosis as strictly as the ketogenic diet.
Dietary Fat
- Ketogenic Diet: Encourages high dietary fat intake, which may not be suitable for everyone.
- Modified Atkins Diet: Offers a more balanced approach, making it more appealing to some individuals.
Protein Intake
- Ketogenic Diet: Restricts protein intake to moderate levels.
- Modified Atkins Diet: Permits higher protein consumption.
Satiety and Food Choices
- Ketogenic Diet: The high-fat content may promote feelings of fullness, but the strict carb restrictions limit food choices.
- Modified Atkins Diet: Offers more dietary flexibility and a broader range of food choices.
External Links for Further Research
For a deeper understanding of the ketogenic diet and the modified Atkins diet, consider exploring these external resources:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Which diet is better for weight loss?
- The ketogenic diet is often more effective for rapid weight loss due to strict carb restrictions and high-fat content.
2. Can I switch between these diets?
- Some individuals may transition between these diets based on their goals and preferences, but it’s advisable to do so under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
3. Are these diets suitable for everyone?
- These diets may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or dietary restrictions. Consult a healthcare provider before starting any new diet plan.
In conclusion, both the ketogenic diet and the modified Atkins diet offer low-carb alternatives for those seeking weight management and potential health improvements. The choice between them depends on your specific goals, dietary preferences, and how your body responds to each approach. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes to ensure they align with your individual needs and health conditions.