Gestational Diabetes: Understanding its Impact on Pregnancy and Effective Management
Pregnancy is a beautiful journey filled with excitement and anticipation. However, it is important to be aware of the potential health risks that can arise during this time, including gestational diabetes (GD). Gestational diabetes is a condition that affects pregnant women, characterized by high blood sugar levels. In this blog post, we will delve into what gestational diabetes is, its effects on pregnancy, and the importance of early detection and management.
Understanding Gestational Diabetes
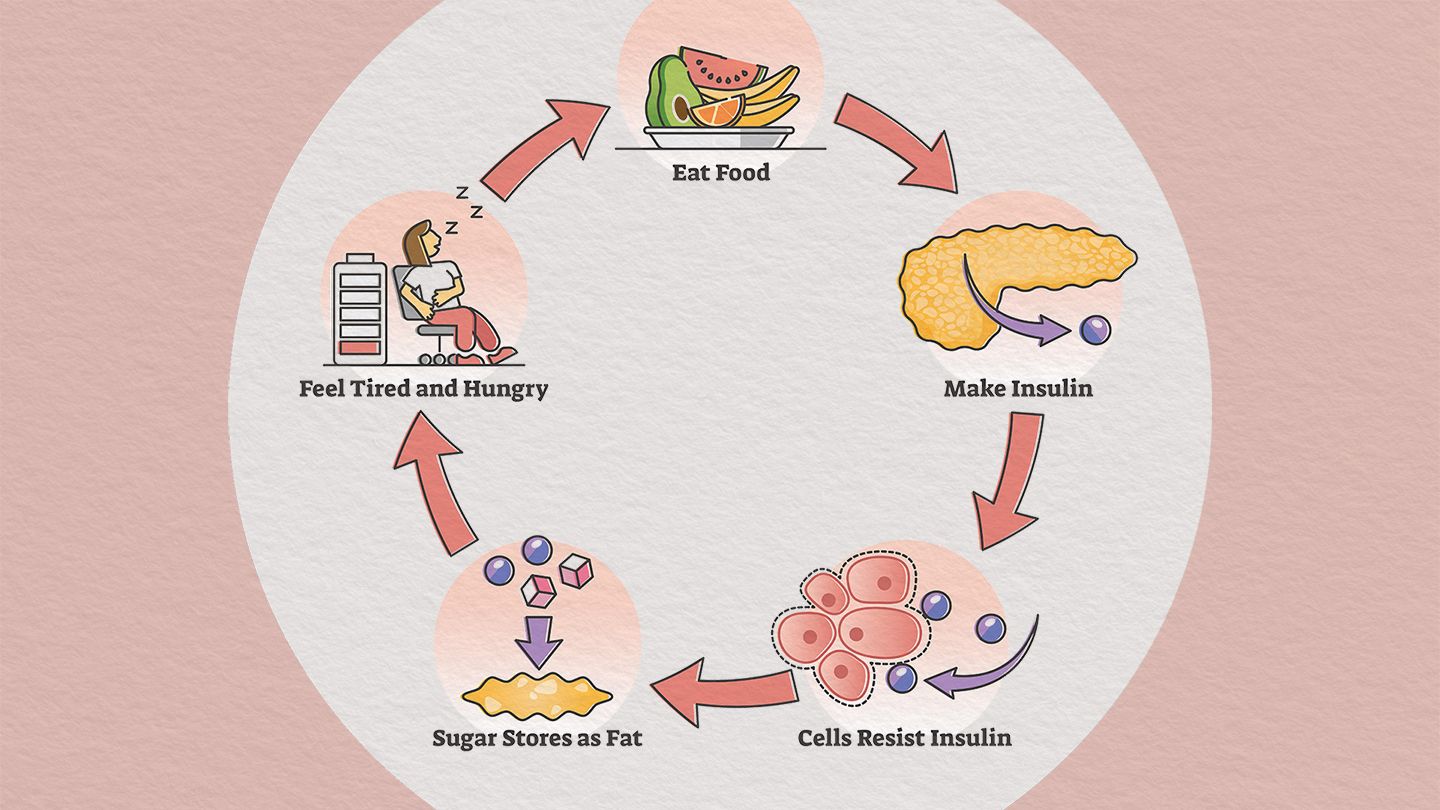
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin or effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. During pregnancy, hormonal changes can lead to insulin resistance, causing blood sugar levels to rise.
Effects of Gestational Diabetes on Pregnancy
Increased Risk of Complications
Untreated or poorly controlled gestational diabetes can lead to various complications during pregnancy. It can increase the risk of preeclampsia, a condition characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs such as the liver and kidneys. It can also lead to premature birth, requiring the baby to be delivered before the full term.
Macrosomia (Large Birth Weight)
High blood sugar levels in the mother can affect the baby’s growth and lead to macrosomia, a condition in which the baby is larger than average. This can increase the risk of complications during delivery, such as shoulder dystocia (when the baby’s shoulders get stuck during birth).
Hypoglycemia in Newborns
Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes may experience low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) shortly after birth. This is because the baby’s pancreas produces extra insulin in response to the high blood sugar levels in the mother’s womb. Prompt monitoring and management are essential to prevent complications in the newborn.
Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Women who develop gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. It is crucial for these women to undergo regular screening for diabetes post-pregnancy and adopt a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk.
Early Detection and Management
Early detection and proper management of gestational diabetes are key to minimizing its effects on both the mother and the baby. Here are some important aspects of managing gestational diabetes:
Regular Glucose Testing
Pregnant women are usually screened for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. If risk factors are present, the screening may be done earlier. The screening involves a glucose challenge test followed by a glucose tolerance test to confirm the diagnosis.
Medical Supervision and Care
Once diagnosed, it is crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals, including obstetricians, endocrinologists, and dietitians. They will provide guidance on blood sugar monitoring, meal planning, and lifestyle modifications.
Balanced Diet
Following a well-balanced diet is essential in managing gestational diabetes. This includes consuming complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber-rich foods. Portion control and avoiding sugary and processed foods are also important.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity, as advised by healthcare professionals, can help improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. Activities like walking, swimming, and prenatal exercises are generally safe during pregnancy.
Medication or Insulin Therapy
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient to manage gestational diabetes. Medication or insulin therapy may be prescribed by healthcare professionals to control blood sugar levels effectively.
Effects of Gestational Diabetes on Pregnancy
Increased Risk of Gestational Hypertension
Gestational diabetes can contribute to the development of gestational hypertension, a condition characterized by high blood pressure during pregnancy. This can increase the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
Polyhydramnios
Gestational diabetes can lead to an excess accumulation of amniotic fluid, a condition called polyhydramnios. This can cause discomfort for the mother and increase the risk of preterm labor or other complications during delivery.
Increased Risk of C-Section
Women with gestational diabetes may have an increased likelihood of delivering via cesarean section. This can be due to factors such as a larger baby size, difficulties during labor, or concerns about the baby’s well-being.
Development of Type 2 Diabetes
Women who have had gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. It is important for these women to undergo regular follow-up screenings and adopt healthy lifestyle habits to reduce their risk.
Future Health Implications for the Baby
Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes have a higher risk of developing obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life. It highlights the importance of managing gestational diabetes to ensure the long-term health of the child.
Importance of Early Detection and Management
Early detection and proper management of gestational diabetes are crucial to minimize its effects on both the mother and the baby. Here are some key reasons why early detection and management are essential:
Optimal Blood Sugar Control
Early detection allows for timely interventions, such as dietary changes, exercise, and medication if necessary. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, reducing the risks associated with uncontrolled gestational diabetes.
Prevention of Complications
Effective management of gestational diabetes helps minimize the risk of complications such as preeclampsia, preterm birth, and macrosomia. It promotes a healthier pregnancy for both the mother and the baby.
Improved Pregnancy Outcomes
By managing gestational diabetes, women can increase the chances of having a vaginal delivery and reduce the need for interventions like cesarean sections. It also contributes to overall better health outcomes for the baby.
Long-Term Health Benefits
Early detection and management of gestational diabetes can have lasting effects on the health of the mother and the baby. By reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and obesity, it sets the foundation for a healthier future.
Gestational diabetes is a condition that requires careful management to ensure a healthy pregnancy and reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby. Early detection, proper medical supervision, a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and adherence to the recommended treatment plan are essential. By taking proactive steps, pregnant women with gestational diabetes can navigate their pregnancy journey with confidence and promote the well-being of themselves and their babies.