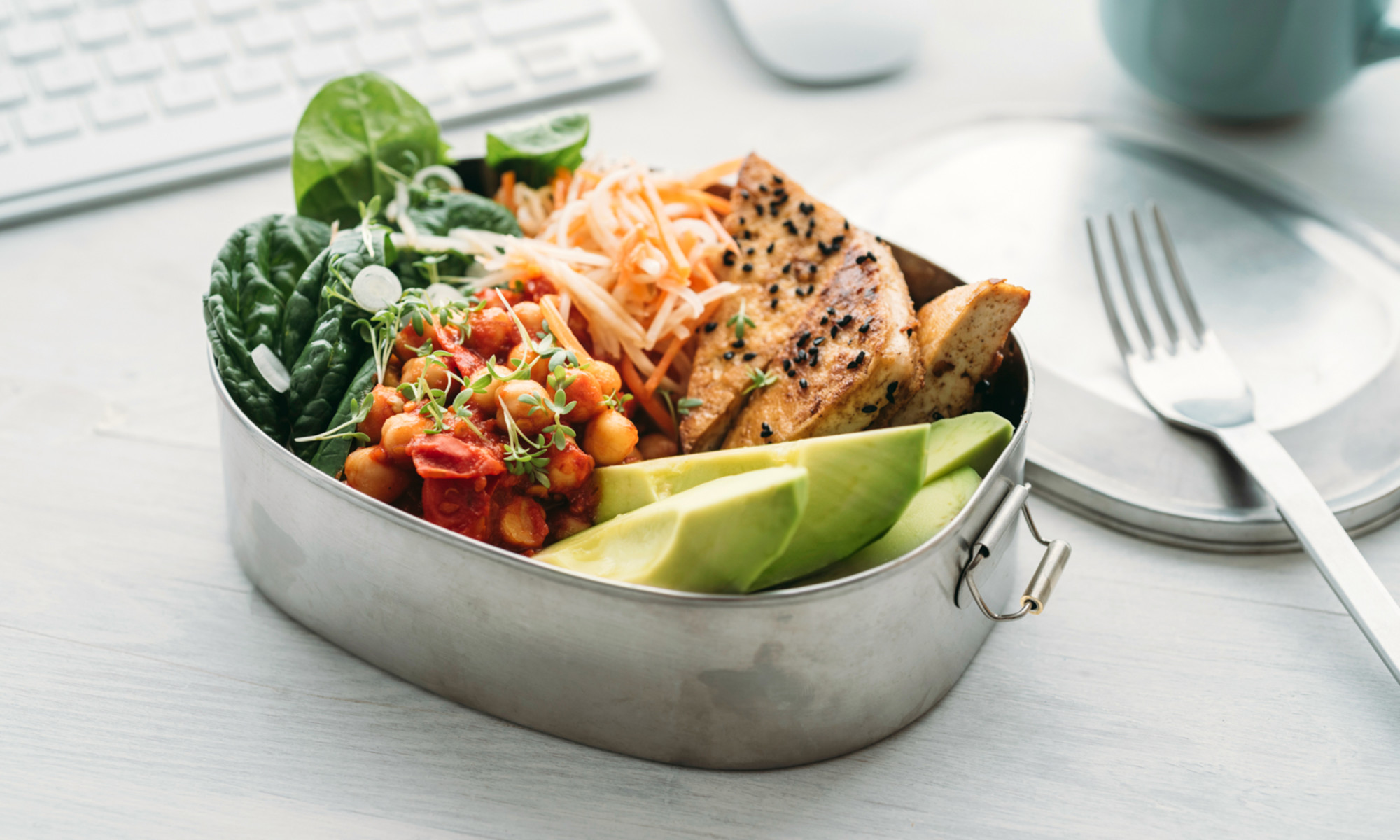
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it can be a complex and challenging condition to manage, one of the most powerful tools at your disposal is your diet. A balanced diet plays a crucial role in helping individuals with diabetes maintain stable blood sugar levels and lead healthier lives. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the science behind a balanced diet for diabetes and how nutrient-rich foods can positively impact blood sugar levels.
Understanding Diabetes
Before delving into the specifics of a balanced diet, it’s essential to understand the basics of diabetes. There are two primary types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2.
- Type 1 Diabetes: This is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with Type 1 diabetes require insulin therapy to regulate their blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This form of diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin. Initially, the pancreas produces extra insulin, but over time, it can’t keep up. Lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and medication, are typically used to manage Type 2 diabetes.
The Role of Diet in Diabetes Management
A balanced diet is a cornerstone of diabetes management, regardless of the type. It’s all about making informed choices that help regulate blood sugar levels. The key components of a diabetes-friendly diet include:
1. Carbohydrate Management:
- Complex Carbohydrates: Foods like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables contain complex carbohydrates that are broken down slowly, leading to more stable blood sugar levels.
- Fiber: High-fiber foods, such as oats and beans, not only slow digestion but also improve overall blood sugar control.
- Monitoring Portions: Controlling the portion sizes of carbohydrate-rich foods is vital.
2. Protein Selection:
- Lean protein sources, such as poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes, help regulate blood sugar and provide a feeling of fullness.
3. Healthy Fats:
- Unsaturated fats, found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can improve insulin sensitivity.
4. Limiting Added Sugars:
- Minimizing the consumption of sugary foods and beverages is crucial.
5. Balancing Meals:
- Creating balanced meals that include carbohydrates, protein, and fats can help maintain steady blood sugar levels.
6. Frequent, Consistent Eating:
- Spreading meals and snacks evenly throughout the day prevents blood sugar spikes and crashes.
The Science of Nutrient-Rich Foods
The science behind a balanced diet for diabetes revolves around nutrient-rich foods that impact blood sugar levels in favorable ways:
1. Fiber:
Fiber, particularly soluble fiber, is a powerful tool for blood sugar control. It slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar. Foods high in fiber include oats, beans, fruits, and vegetables.
2. Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and walnuts, have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation, benefitting individuals with diabetes.
Monounsaturated Fat vs. Polyunsaturated Fat: Exploring the Differences
3. Chromium:
Chromium is a mineral that plays a role in insulin action. It is found in foods like broccoli, barley, and green beans.
4. Magnesium:
Magnesium is essential for glucose metabolism. Leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains are excellent sources of magnesium.
5. Protein:
Protein-rich foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels by reducing the impact of carbohydrates. Lean sources of protein, such as poultry, fish, and tofu, are ideal choices.
External Links
For further insights and expert advice on managing diabetes through diet, consider exploring these external resources:
- American Diabetes Association – Food and Fitness
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases – Eating, Diet, & Nutrition for Diabetes
- Mayo Clinic – Diabetes Diet: Create Your Healthy-Eating Plan
What You Cannot Eat on the DASH Diet: Making Heart-Healthy Choices
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I still enjoy sweets in moderation if I have diabetes?
Yes, you can enjoy sweets in moderation, but it’s crucial to account for them within your carbohydrate and calorie intake. Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for guidance.
2. Should I follow a specific diet plan for diabetes, such as the Mediterranean or DASH diet?
Diet plans like the Mediterranean and DASH diets can be excellent choices for individuals with diabetes. They emphasize nutrient-rich foods and can help manage blood sugar levels.
3. Is it essential to count carbohydrates with every meal?
Counting carbohydrates is a common practice in diabetes management. It helps individuals understand how different foods affect their blood sugar and allows for more precise meal planning.
4. Can exercise be as crucial as diet in managing diabetes?
Physical activity is a fundamental component of diabetes management. Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
A balanced diet is a powerful ally in managing diabetes and promoting overall well-being. The science behind a diabetes-friendly diet is grounded in the positive impact of nutrient-rich foods on blood sugar control. By making informed choices about the types and amounts of foods you consume, you can play an active role in managing your diabetes effectively. It’s crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals and registered dietitians to create a personalized dietary plan that meets your unique needs. A balanced diet, combined with other aspects of a healthy lifestyle, can help you live a fulfilling life while effectively managing your diabetes.