Type 2 Diabetes Before Age 60 Increases Dementia Risk by 300%, Study Finds
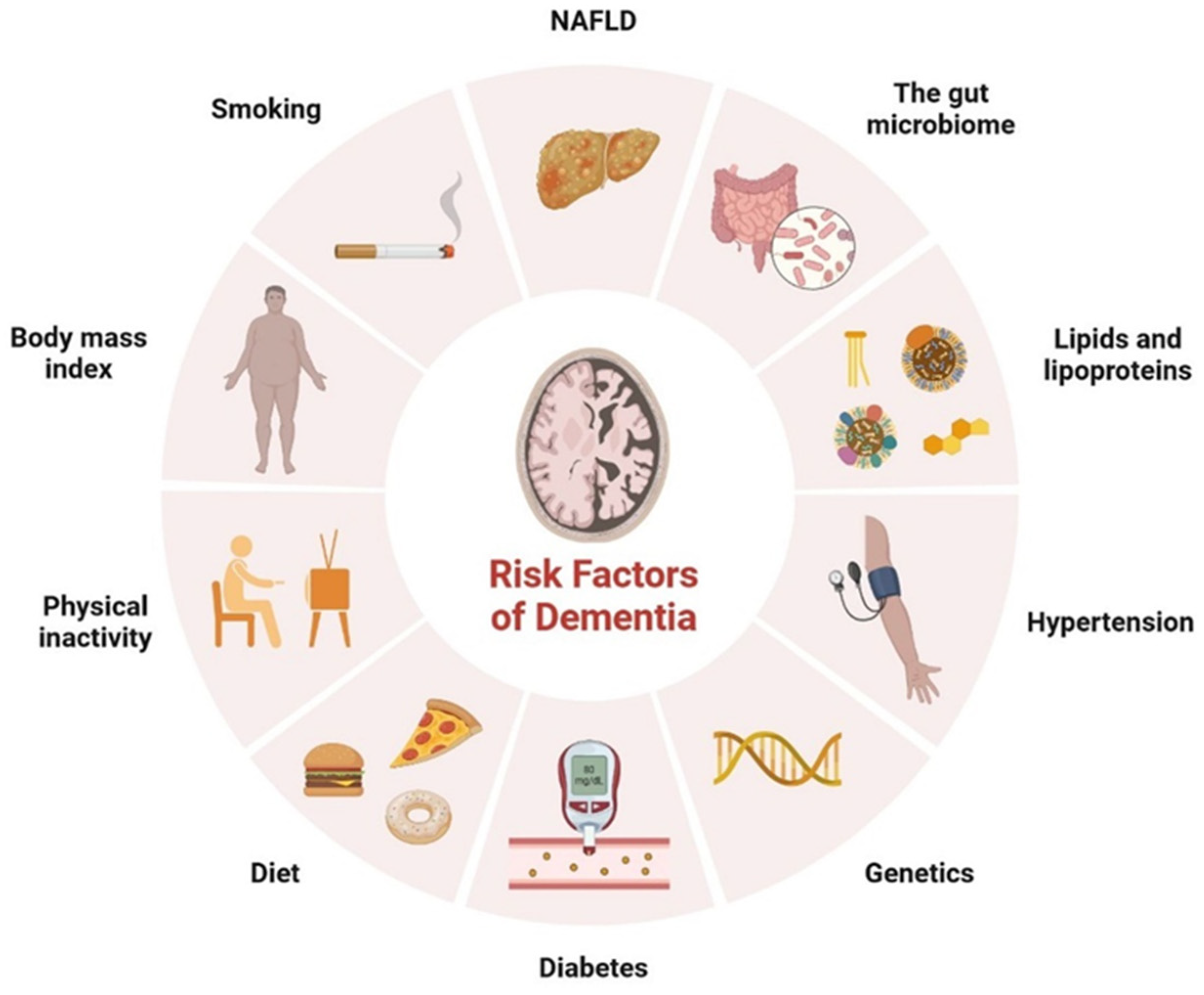
In recent years, there has been a growing concern regarding the impact of type 2 diabetes on cognitive health. While it is well-known that diabetes can lead to various complications, including heart disease and kidney problems, emerging research suggests a potential link between type 2 diabetes and an increased risk of developing dementia. A groundbreaking new study has shed light on this connection, revealing that a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes before the age of 60 may significantly raise the risk of dementia by a staggering 300%. This finding highlights the importance of early diabetes management and the need for increased awareness surrounding the potential long-term consequences of the disease.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes and Dementia
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by the body’s inability to effectively use insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels. It affects millions of people worldwide and is often associated with obesity, poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and genetic factors. Dementia, on the other hand, is a general term for a decline in cognitive function, affecting memory, thinking, and behavior. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia, accounting for approximately 60-80% of cases.
Delicious and Nutritious Juices for Diabetics: A Refreshing Path to Health
The Study and its Findings
The recent study, conducted by a team of researchers from a renowned medical institution, involved a large-scale analysis of medical records of individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. The study followed participants for over a decade, examining their health outcomes and assessing the relationship between diabetes and dementia risk.
The results of the study revealed a striking association between an early diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and an increased risk of developing dementia. Participants diagnosed with diabetes before the age of 60 were found to have a threefold higher risk of dementia compared to those diagnosed after the age of 60 or without diabetes. This finding held true even after accounting for various factors such as age, sex, educational level, and cardiovascular health.
Potential Mechanisms
Researchers have proposed several mechanisms to explain the observed link between type 2 diabetes and dementia. Chronic high blood sugar levels and insulin resistance, common in diabetes, may contribute to the accumulation of toxic proteins in the brain, leading to the development of dementia. Additionally, vascular damage caused by diabetes could impair blood flow to the brain, contributing to cognitive decline.
Implications and Recommendations
The study’s findings have significant implications for both individuals and healthcare providers. Firstly, it emphasizes the importance of early diabetes detection and intervention. Timely diagnosis and effective management of type 2 diabetes, including lifestyle modifications and appropriate medication, can help reduce the risk of complications, including dementia.
Moreover, healthcare professionals should prioritize regular cognitive assessments for individuals with type 2 diabetes, particularly those diagnosed before the age of 60. Identifying early signs of cognitive decline can enable timely interventions and support, potentially mitigating the risk of developing dementia.
Submariner Full Black Gold watch
For individuals with type 2 diabetes, adopting a healthy lifestyle becomes even more crucial. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and controlling blood sugar levels are vital in reducing the risk of complications, including dementia.
Public health campaigns and educational initiatives should aim to increase awareness about the potential link between type 2 diabetes and dementia. This knowledge can empower individuals to make informed choices about their health and motivate them to take proactive measures to manage their diabetes effectively.
The new study’s findings underscore the importance of recognizing the long-term consequences of type 2 diabetes and the potential impact it may have on cognitive health. With the number of people diagnosed with diabetes increasing worldwide, it is crucial to prioritize prevention, early detection, and effective management of the condition. By doing so, we can work towards reducing the risk of complications, including dementia, and promoting better overall health and well-being.