Understanding IBS Symptoms: What You Need to Know
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common and often misunderstood digestive condition. It can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, causing symptoms like abdominal pain, cramping, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of IBS, covering its signs and symptoms, potential causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
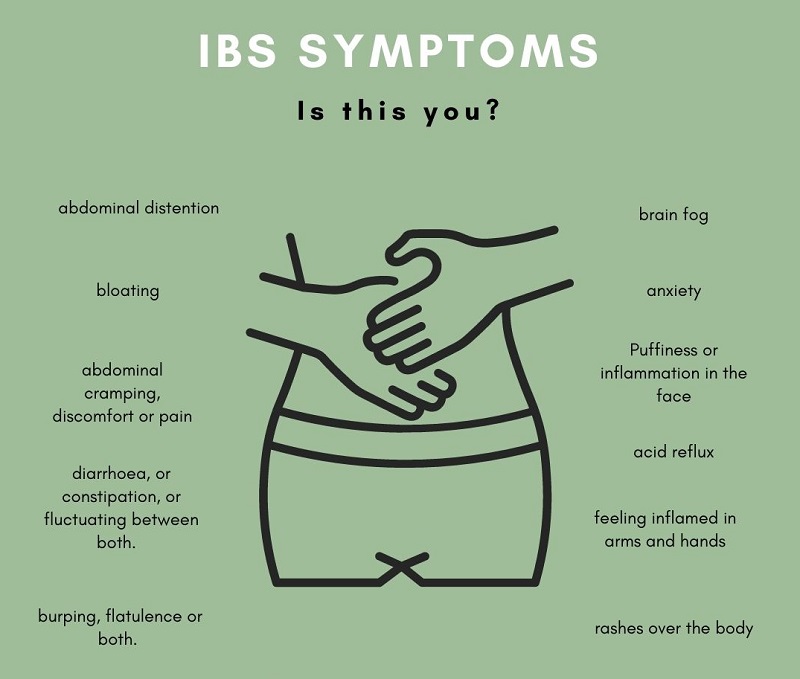
What are the signs and symptoms of IBS? IBS manifests differently from person to person, and the symptoms can fluctuate over time. Common indicators include:
- Abdominal Pain or Discomfort: Often tied to bowel movements, this discomfort can range from mild to severe.
- Changes in Bowel Movements: IBS can lead to shifts in the frequency and consistency of bowel movements, causing diarrhea, constipation, or a combination of both.
- Bloating and Gas: Excess gas production and abdominal bloating are frequent complaints among those with IBS.
- Mucus in Stool: Some individuals may notice the presence of mucus in their stool.
- Feeling of Incomplete Evacuation: After a bowel movement, some individuals may still feel as if they haven’t completely emptied their bowels.
In addition to these primary symptoms, IBS can also be accompanied by secondary issues such as nausea, vomiting, headaches, backaches, fatigue, insomnia, anxiety, or depression. The severity and duration of these symptoms can vary depending on factors like stress, diet, hormonal changes, and medication usage.
What are the possible causes and triggers of IBS? While the precise cause of IBS remains elusive, it is believed to arise from a complex interplay between the brain, the gut, and environmental factors. Potential contributors and triggers include:
- Intestinal Muscle Abnormalities: Irregular muscle contractions in the intestines can contribute to IBS symptoms.
- Abnormal Nerve Signals: Hypersensitivity or abnormal nerve signals within the gut can amplify discomfort.
- Inflammation and Infections: Inflammation or infections in the intestine may lead to IBS symptoms.
- Gut Microbiota Imbalance: Changes or imbalances in gut bacteria can play a role.
- Food Intolerances or Allergies: Sensitivities to certain foods, such as lactose, gluten, or FODMAPs, can trigger IBS symptoms.
- Stress and Emotional Distress: Psychological factors, like stress and emotional distress, can exacerbate symptoms.
Common triggers include consuming foods high in fat, sugar, caffeine, alcohol, dairy, gluten, or spices. Medications that affect gut motility or bacteria, changes in routine or environment, lack of sleep or exercise, and hormonal fluctuations (particularly in women) can also provoke symptoms.
“Honey and Fructose: Exploring the Sweet Truth About Nature’s Golden Elixir”
How is IBS diagnosed and treated? Diagnosing IBS primarily involves a comprehensive evaluation of medical history, physical examination, and symptom criteria. Additionally, doctors may perform tests to rule out other conditions that share similar symptoms, including blood tests, stool tests, breath tests, and imaging studies.
Treatment for IBS aims to alleviate symptoms and enhance the individual’s quality of life, as there is no known cure. Treatment options include:
- Dietary Modifications: Identifying and avoiding trigger foods while increasing fiber intake.
- Probiotics: Supplements can help restore a balanced gut microbiome and reduce inflammation.
- Medications: Depending on symptoms, medications may be prescribed to control diarrhea, constipation, pain, or spasms.
- Psychological Therapies: Strategies to manage stress and emotional well-being can be beneficial.
- Alternative Therapies: Some individuals find relief through practices like acupuncture, yoga, meditation, or hypnotherapy.
The treatment plan is highly individualized, tailored to the type and severity of symptoms, as well as the patient’s preferences and response to therapies. Finding the optimal combination of treatments may require some experimentation.
In conclusion, IBS is a complex condition that can significantly impact one’s life. Understanding its symptoms, potential causes, and treatment options is crucial for those affected by this digestive disorder. With proper management and guidance from healthcare professionals, individuals with IBS can often achieve symptom relief and improve their overall well-being.