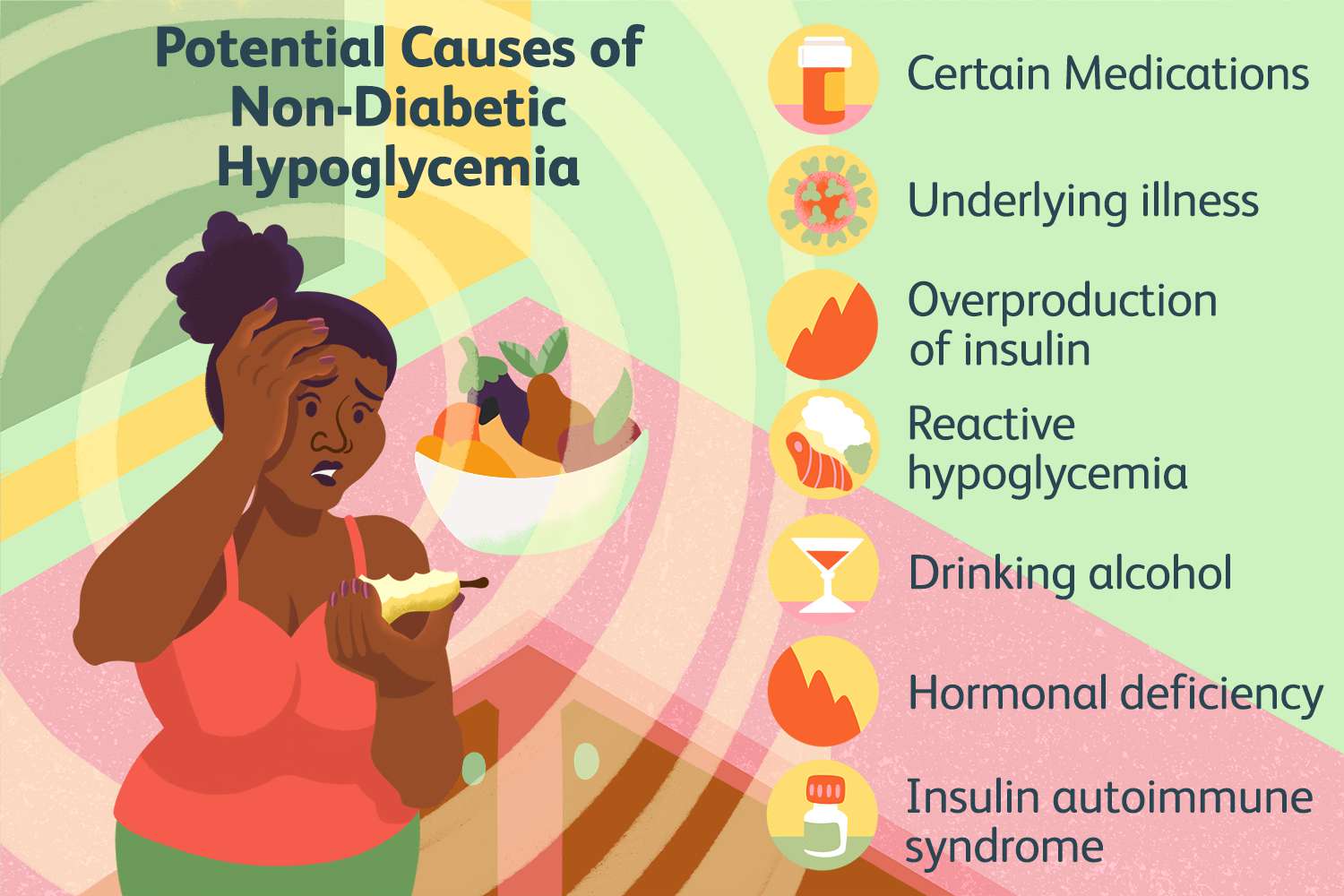
What Causes Low Blood Sugar Without Diabetes? Exploring the Underlying Factors
Low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia, is commonly associated with diabetes. However, it’s important to note that low blood sugar can occur in individuals without diabetes as well. If you’ve experienced episodes of low blood sugar without a diabetes diagnosis, understanding the potential causes is crucial for identifying the underlying factors. In this blog post, we will explore some possible causes of low blood sugar in non-diabetic individuals and discuss when it’s essential to seek medical attention.
Reactive Hypoglycemia
Reactive hypoglycemia is characterized by a drop in blood sugar levels a few hours after consuming a meal high in carbohydrates. It occurs when the body releases an excess amount of insulin in response to a sudden surge in blood sugar. This can lead to symptoms of low blood sugar, such as shakiness, dizziness, and sweating.
Medications
Certain medications, such as those used to treat high blood pressure (beta-blockers) or certain antibiotics, can interfere with blood sugar regulation and potentially cause episodes of low blood sugar. If you suspect that your medication may be contributing to low blood sugar, consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can lead to a drop in blood sugar levels. Alcohol inhibits the liver’s ability to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, resulting in hypoglycemia. It’s important to consume alcohol in moderation and be mindful of its potential effects on blood sugar.
How to Manage Stress and Anxiety: Tips and Techniques for a Balanced Life
Hormonal Imbalances
Certain hormonal imbalances, such as an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or adrenal insufficiency, can affect blood sugar regulation. These conditions may cause fluctuations in hormone levels, including insulin, leading to low blood sugar episodes.
https://unisexstuff.com/collections/best-top10-luxury-womens-watches/products/missfox-fashion-bling-casual-female-quartz-crystal-diamond-leopard-watch?ref=2aqt7yi0
Insulinoma
In rare cases, a noncancerous tumor called an insulinoma may develop in the pancreas. This tumor produces excessive amounts of insulin, leading to recurrent episodes of low blood sugar. If you experience frequent and unexplained episodes of hypoglycemia, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Intense Physical Activity
Engaging in intense or prolonged physical activity without adequate fueling can deplete the body’s glycogen stores, leading to low blood sugar levels. It’s important to maintain a balanced diet and ensure proper carbohydrate intake to support energy levels during exercise.
Skipping Meals
Skipping meals or having long gaps between meals can contribute to low blood sugar. Without a regular supply of glucose from food, the body’s blood sugar levels can drop, causing symptoms of hypoglycemia. Eating balanced meals and snacks at regular intervals can help prevent these episodes.
Certain Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as liver disease, kidney disorders, or pancreatic tumors, can affect the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. These conditions may interfere with glucose production or utilization, leading to episodes of hypoglycemia.
Malnutrition or Poor Diet
A diet lacking in adequate nutrients, particularly carbohydrates, can contribute to low blood sugar levels. Insufficient calorie intake or imbalanced macronutrient distribution can deprive the body of the necessary fuel to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Reactive Hypoglycemia after Gastric Surgery
Individuals who have undergone gastric bypass surgery or other types of weight loss surgery may experience reactive hypoglycemia as a result of rapid digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. This can lead to an excessive release of insulin and subsequent episodes of low blood sugar.
Metabolic Disorders
Certain metabolic disorders, such as glycogen storage diseases or disorders of fatty acid oxidation, can impact the body’s ability to store and utilize glucose effectively. These conditions may lead to episodes of hypoglycemia even in the absence of diabetes.
Stress and Anxiety
Prolonged or chronic stress can affect blood sugar regulation. Stress hormones like cortisol can increase insulin production and cause blood sugar levels to drop. Similarly, anxiety or panic attacks can trigger the release of stress hormones and lead to episodes of low blood sugar.
Experiencing low blood sugar without a diabetes diagnosis can be puzzling. Various factors, including reactive hypoglycemia, certain medications, excessive alcohol consumption, hormonal imbalances, insulinoma, intense physical activity, and skipping meals, can contribute to episodes of low blood sugar in non-diabetic individuals. If you’re frequently experiencing symptoms of hypoglycemia, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. They can conduct thorough evaluations and provide guidance to help manage and prevent low blood sugar episodes effectively.